What is the thickness of the geomembrane?

There are numerous misconceptions regarding what makes an optimally constructed geomembrane in the geomembrane sector. One of the most important is the needed thickness, which frequently leads to a debate among geomembrane specialists and engineers: “Is a thicker membrane genuinely better?”
Geomembrane is a plastic construction material product, which is waterproof, dense, and used for drainage control projects to have an impermeable containment or barrier.
Geomembrane is one sort of geosynthetics product, with excellent Geomembrane properties and a competitive price advantage. It is used in various industries, water management, oil gas, environment, aquaculture, and agriculture.
Ocean Global Geomembrane is made of polyethylene resin at a special formula; our products include HDPE Geomembrane, LLDPE Geomembrane, PVC Geomembrane, EDPM Geomembrane, RPP Geomembrane, and TRP Geomembrane, all the products use 100% stainless material, no recycled secondary material.
HDPE Geomembrane refers to rich-density polyethylene film used in civil anti-seepage projects. The thickness of the HDPE Geomembrane used in anti-seepage and waterproof projects ranks from 0.5mm to 3.0mm. The thickness may be 0.75mm, 1.0mm, 1.25mm, 1.5mm, 2.0mm, 2.5mm, 3.0mm, 3.5mm, etc. Apply hot-melt welding equipment for joint processing.
Table of Contents
The Present Situation
A typical geomembrane is 60 mils thick and has the consistency of a thicker waste bag. The industry standard for this material is 60 mil HDPE. Many engineers are taught that a thicker geomembrane is a better geomembrane, although this is not always the case.
The chemical and UV resistance of XR geomembranes impresses the XR Geomembrane Engineers, however, they frequently request that the geomembranes be 60 mils thick rather than 30 mils, which is too thin for a geomembrane. Because they’re strengthened with an internal reinforcing foundation fabric that gives high strength and puncture resistance, the average XR Geomembrane material used for lining projects is 30 mils thick. Unreinforced geomembranes, such as HDPE, on the other hand, become increasingly puncture resistant as their thickness increases. The distinction is in XR Geomembranes’ unique manufacturing method, which allows them to be thin while yet being incredibly robust.
Puncture resistance and tensile strength
The foundation fabric, or “scrim,” determines the tensile strength of an XR Geomembrane. The XR Geomembrane can only extend 20–25 percent, but a conventional HDPE geomembrane may stretch up to 200–300 percent. The HDPE geomembrane gives fast, however, an XR Geomembrane, which is reinforced, can withstand a significantly higher tensile strain and has a yield and breaking point of roughly 25% elongation.
Environmental Stress and Life Expectancy
A thicker geomembrane would seem to have a longer life expectancy. In actuality, a geomembrane’s thickness has minimal bearing on its lifespan. The strength and geomembrane manufacturing procedure determine its real lifespan. When it comes to environmental stress, many people believe that a thicker geomembrane is the way to go. The XR-5 Geomembrane, on the other hand, is more puncture resistant and less prone to wear and tear.
HDPE Geomembrane liners
The thickness of the anti-seepage Geomembrane is usually designed during the engineering design. There are many aspects considered in the design: local environment, external factors, water depth, etc. The design thickness of the Geomembrane is also similar to the material and form of the soil. For example, the longer the diameter and angularity of the soil particles of sandy soil, the greater the thickness required.
The thickness of the Geomembrane opted for a different application field is also different. There are many used fields, such as municipal environmental protection field landfills, especially liquid waste, which has fluidity and extravasations and is simple to spread and difficult to control and handle. Now, Geomembrane can be used to solve this problem, generally, 1.5mm or 2mm thick Geomembrane is used in landfills.
Certainly, when Geomembrane is used in different directions in the landfill, the thickness of the Geomembrane is different, as a substrate for anti-seepage, side slope anti-seepage, and closure coverage. The categories of films used in different orientations are different, such as smooth surfaces for substrates and rough surfaces for slopes.
Farming Field
Geomembranes are used in the field of tray agriculture. As water seepage often occurs in diversion ditches, geomembranes can be used now to protect the extravasations of irrigation water and improve efficiency and longevity. Also, there are tray agriculture fish ponds and shrimp ponds. Geomembranes with a thickness of 0.75 mm and 1 mm are used.

Petrochemical Industry
The durability, acid resistance, alkali resistance, and chemical resistance of Geomembrane make it very popular in the petrochemical industry. It can be applied for anti-seepage in chemical sewage plants and oil refining sewage tanks to avoid chemically corrosive liquids and petroleum waste liquids. For diffusion and extravasations, these projects generally use Geomembrane with a thickness of 1.5mm, 2mm, or 2.5mm.
In addition, in the choice of thickness, there are many other aspects, such as landfill topography, soil quality, anti-seepage materials, anti-seepage requirements, and so on. How to select the thickness of the Geomembrane in anti-seepage engineering? There is no doubt that the thicker the Geomembrane, but at the same time the cost will expand. The thinner the thickness, despite the cost can be reduced; it cannot meet the needs of the project.
Therefore, choosing a suitable thickness for the Geomembrane can not only meet engineering needs but also complete the purpose of reducing costs. The Geomembrane thickness should be chosen and customized according to the engineering requirements of the Geomembrane. The thickness of the Geomembrane is generally not less than 0.5mm.
In the actual operation of the project, it is suggested to entrust the relevant testing center to test the materials to check whether the quality of the Geomembrane produced by the manufacturer is decent and to provide a basis for selecting safe, reliable, and economical materials. The application environment of the Geomembrane is buried in the ground all year round, so it is required to have good anti-aging and anti-decomposition ability and can withstand the piercing of plant roots. For Geomembrane working in a complex water environment, it should further have good acid and alkali resistance.
Puncture-Proof Pack
When analysing and comparing geomembrane materials, the facts and figures surrounding this thickness disagreement are critical. When displaying the ultimate strength of the XR Geomembrane, however, having actual proof that supports this “less is more” philosophy is far more successful. This is why XR Geomembranes created a puncture pack with three distinct geomembranes: 60 mil HDPE, 45 mil Polypropylene, and 30 mil XR-5.
The puncture pack’s actual demonstration of the XR Geomembrane’s superior tensile and puncture strengths might eventually illustrate that a thicker geomembrane is not necessarily the best choice for your needs when deciding between the three geomembranes.
“Material thickness should be determined by design, which requires site-specific knowledge and considerations. Although various thicknesses, such as 30 and 60, are permitted (Page V), we feel that this method restricts the designer’s options, forces the use of generic designs, and may result in higher total project costs. We also think, and propose to consultants, that a minimum thickness of material type be set first, followed by letting the consultants “create” the system. The following are our suggestions based on seamability, puncture ability, and installability: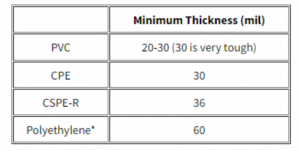
*Polyethylene is specified at a minimum thickness of 60 mil for seamability reasons. It has not been proved to us that PE materials with a thickness of less than 60 mil can be seamed consistently in the field. There is also worry that this is the bottom limit for establishing stress-cracking-friendly circumstances. While stress cracking is currently being investigated, seaming techniques are beginning to improve. It’s worth noting that the West Germans now demand PE thicknesses of more than 100 mil.”
The foregoing is transcribed precisely as the EPA gave it to the Corps. The EPA is worried, as you can see from this conversation, that generic designs based only on material thickness specifications might be not only expensive but also harmful in many cases. To guarantee secure confinement, the design engineer must have the freedom to use the most effective material. The requirement of a minimum 60 mil thickness regardless of material does not motivate designers to enhance their work. The EPA is worried about PE seaming below 60 mil Geomembrane thickness (HDPE, VLDPE, LLDPE). PVC, CPE, and CSPE-R, on the other hand, do not have this problem. For example, designs made of 20 or 30 mm PVC can provide extremely effective, secure, and cost-efficient containment solutions.
HDPE geomembrane is a type of anti-seepage film made of high-density polyethylene. HDPE Geomembrane thickness utilised in anti-seepage and waterproofing applications range from 0.5mm to 3.0mm. 0.75mm, 1.0mm, 1.25mm, 1.5mm, 2.0mm, 2.5mm, 3.0mm, 3.5mm, and more thicknesses are possible. For joint processing, use hot-melt welding equipment.
In most cases, the thickness of the anti-seepage geomembrane is determined during the engineering design process. Many aspects are taken into account in the design, including the local environment, external forces, water depth, and so on. The substance and shape of the soil have an impact on the geomembrane design thickness. The bigger the diameter and angularity of the soil particles in sandy soil, for example, the greater the needed thickness.
The thickness of the geomembrane used for various application domains varies as well. Many fields are employed, such as municipal environmental protection field dumps, particularly liquid waste, which has fluidity and extravasation, is easy to spread, and is difficult to monitor and treat. Now, geomembrane may be utilised to remedy this problem; most landfills employ 1.5mm or 2mm thick geomembrane. Of course, the thickness of geomembrane used as a substrate for anti-seepage, side slope anti-seepage, and closing coverage varies when utilised in different directions in the landfill.
Aquaculture is one of the fields where geomembranes are employed. Geomembranes may be utilised currently to reduce irrigation water extravasation and enhance efficiency and longevity in diversion ditches, where water seepage is common. There are also shrimp ponds and aquaculture fish ponds. Geomembranes of 0.75mm and 1mm thickness are employed.
Geomembrane is particularly popular in the petrochemical sector because of its impermeability, acid resistance, alkali resistance, and chemical resistance. It may be used to prevent chemical corrosive liquids and petroleum waste liquids from seeping into chemical sewage facilities and oil refining sewage tanks. These projects often employ Geomembrane thickness of 1.5mm, 2mm, or 2.5mm for diffusion and extravasation.
There are also many additional elements to consider when choosing a thickness, such as landfill topography, soil quality, anti-seepage materials, anti-seepage regulations, and so on. In anti-seepage engineering, how do you pick Geomembrane Thickness? There is no question that the thicker the geomembrane is, the higher the cost will be. The thinner the thickness, the lower the cost, but it cannot match the project’s requirements.
As a result, selecting the appropriate thickness of geomembrane can not only fulfil engineering requirements, but also accomplish the goal of cost reduction. The thickness should be chosen and modified in accordance with the geomembrane’s engineering specifications. The geomembrane is typically not less than 0.5mm thick. It is advised that the materials be tested by the relevant testing centre during the project’s real operation to determine if the quality of the geomembrane supplied by the manufacturer is dependable and to give a foundation for selecting safe, reliable, and cost-effective materials.
FAQs
How do geomembranes resist biological degradation?
Most geomembranes are resistant to biological degradation. However, microbial attack can occur at the exposed surface if proper protection or preventive measures are not taken.
What is the maximum size of geomembrane panels available?
The size of geomembrane panels can vary depending on the manufacturer, but they are typically available in widths ranging from 4 to 8 meters (13 to 26 feet) and can be manufactured in longer lengths.
Are geomembranes suitable for use in saltwater environments?
Yes, geomembranes can be used in saltwater environments, but the specific material and formulation should be selected to ensure resistance to saltwater and marine organisms.
Can geomembranes be used for waterproofing basements or tunnels?
Yes, geomembranes can be used for waterproofing basements, tunnels, or other below-grade structures, providing an effective barrier against water intrusion.
What are the considerations for geomembrane selection in floating cover applications?
When selecting a geomembrane for floating cover applications, factors such as tensile strength, flexibility, UV resistance, and compatibility with the floating cover material should be taken into account.
What are the maintenance requirements for geomembranes?
Geomembranes generally require minimal maintenance. Regular inspections, removal of debris or vegetation, and prompt repair of any damages or leaks are recommended to ensure their long-term performance.



