Geomembrane Cost Per Square Foot
It is easy to lose sight of the big picture when you specify a Geomembrane. There are many factors one must consider to choose the one that best suits your application; however, the cost of a lifetime is ignored.
The Geomembrane with a low original cost might cost you just as much, if not more than, a Geomembrane that costs more decent. Before labeling the check, you should display the real Geomembrane cost by looking at the real costs incurred over the lifespan of the product.
Initial Costs of a Geomembrane
To illustrate this point, this article discusses the differences between high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and ethylene interpolymer alloy (EIA) geomembranes (such as XR-5® Geomembranes). No matter what products you are analyzing, the Geomembrane cost breakdown categories will be rather similar.
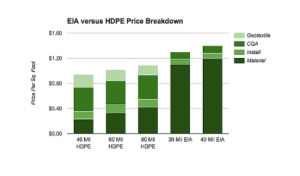
Initial costs can be divided into three main components: equipment, installation, and construction quality assurance costs (CQA). While material costs have a significant impact on the lifetime costs of your Geomembrane, in less expensive cases, a good portion, if not a large portion, of money will be spent on work. Below is a chart showing the key differences.
It is important to note that the cost of the EIA material above includes both shipping and construction. The costs cataloged in this chart, in both geomembranes, are estimated and may vary depending on the size of the project, however. For example, larger projects will have a lower cost of goods and services per square foot. HDPE prices tend to fluctuate frequently, so make sure you reach the right manufacturer when creating your price comparison. Rule CQA 6 — the cost will be much lower for flexible / built geomembranes because there are very few field seams.
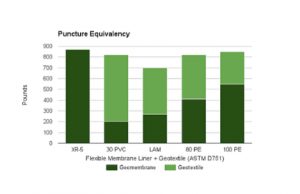
The last part of the price split shows the impact of the cost of adding geotextile to the Geomembrane. EIA geomembranes naturally have high puncture strength, as they can withstand over 800 pounds of ball tip puncture resistance, so they can usually be used without geotextile as depicted in the chart below. Some geomembranes on the market do not have that luxury, however, and require additional items to increase piercing capacity to the same level, leading to additional Geomembrane costs in total installation costs.
The life span should also be considered during this phase. A Geomembrane maintaining a successful performance record for over 30 years might cost more upfront, but the return on investment will be higher than that of a Geomembrane with a lesser initial cost that will only last 10 to 15 years.
Conservation & Reparability
Your Geomembrane should be maintained regularly to maintain optimal performance. The amount of care required varies however from one Geomembrane to another. Some geomembranes, such as HDPE, are prone to environmental stress cracking (ESC), while others, such as the EIA, are made of low-temperature stretchable materials that make these geomembranes more stable. ESC can occur at any time during the senility of your Geomembrane, which means you may need to replace the Geomembrane completely before you can see a return on your investment.
Finally, you should not decide on a Geomembrane based on initial costs. The additional expense will sneak up on you, resulting in a higher lifetime cost. Make sure you do your research and evaluate your options to find a product that fits your performance and budget needs.
FAQs
What materials are commonly used to manufacture geomembranes?
Geomembranes are typically made from materials like high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), and others.
How are geomembranes installed?
Geomembranes are installed by unrolling and deploying them over a prepared subgrade, securing the edges, and often welding or seaming the panels together to create a continuous barrier.
What are the main functions of geomembranes?
Geomembranes primarily serve as barriers to prevent seepage, leakage, and contamination in applications such as landfills, ponds, reservoirs, mining, and agricultural systems.



